Picture this: You’re scrolling through social media when a stunning animated video stops you mid-scroll. Within seconds, you’re hooked, watching until the end, and maybe even sharing it with friends. This is the incredible power of animation in multimedia – it doesn’t just communicate; it captivates, educates, and transforms ordinary content into extraordinary experiences.
In today’s digital landscape, where attention spans are shorter than ever, animation has become the secret weapon for creating compelling multimedia projects. Whether you’re a content creator, educator, marketer, or business owner, understanding how animation enhances multimedia can revolutionise your approach to communication and engagement.
This comprehensive guide explores the transformative role of animation in multimedia projects, revealing why it’s become an indispensable tool for modern digital storytelling and how you can harness its power to create more impactful content.
Table of Contents
What is Animation?
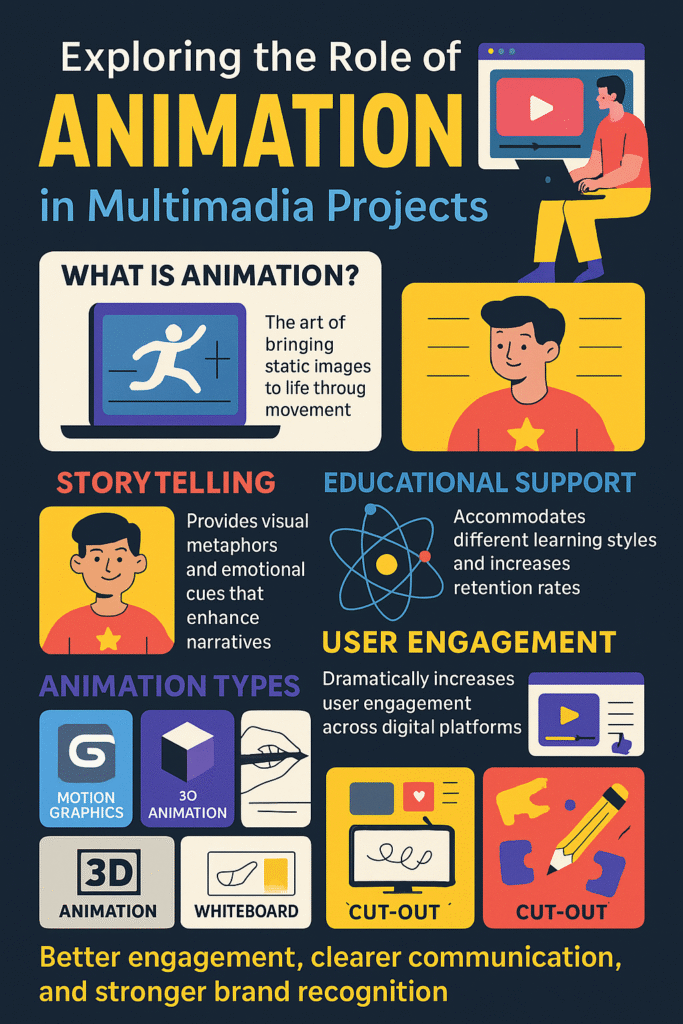
Animation is the art of bringing static images to life through the illusion of movement. At its core, animation involves creating a sequence of images or frames that, when played rapidly, create the perception of continuous motion. This technique has evolved from traditional hand-drawn cartoons to sophisticated computer-generated imagery (CGI) and motion graphics.
Modern animation encompasses various techniques including 2D animation, 3D modeling, stop-motion, motion graphics, and interactive animations. Each method serves different purposes and audiences, from simple logo animations that enhance brand recognition to complex 3D visualizations that explain intricate scientific concepts.
The fundamental principle remains the same: animation transforms static content into dynamic, engaging experiences that capture attention and convey information more effectively than traditional media alone. When integrated into multimedia projects, animation becomes a powerful communication tool that transcends language barriers and appeals to diverse learning styles.
Understanding Animation in Multimedia
Animation in multimedia refers to the strategic integration of animated elements within various digital media formats including videos, presentations, websites, mobile applications, and interactive content. Unlike standalone animations, multimedia animation works synergistically with other elements such as text, audio, photography, and video to create cohesive, immersive experiences.
The role of animation in multimedia extends far beyond entertainment. It serves as a bridge between complex ideas and audience understanding, making abstract concepts tangible and memorable. Modern multimedia projects utilise animation to direct user attention, illustrate complex processes, showcase products, and foster emotional connections with their audiences.
Storytelling
Animation excels at narrative construction in multimedia projects by providing visual metaphors and emotional cues that enhance storytelling. Through character development, scene transitions, and visual effects, animation helps creators build compelling narratives that resonate with audiences on multiple levels.
Animated storytelling in multimedia allows for creative freedom impossible with live-action content. Complex historical events can be visualised, future scenarios can be explored, and abstract concepts can be personified. This versatility makes animation invaluable for documentary filmmakers, journalists, and content creators who need to explain complex topics in accessible ways.
The Adobe Creative Suite has revolutionised how creators approach animated storytelling, providing tools that integrate seamlessly across different multimedia platforms. This technological advancement has democratized animation production, enabling smaller teams to create professional-quality animated content.
Educational Support
In educational multimedia projects, animation serves as a powerful learning aid that accommodates different learning styles. Visual learners benefit from animated diagrams and process illustrations, while kinesthetic learners engage with interactive animated elements that respond to user input.
Research shows that animated educational content increases retention rates by up to 65% compared to static materials. This improvement occurs because animation activates multiple cognitive pathways simultaneously, creating stronger memory associations and deeper understanding.
Educational institutions increasingly incorporate animated elements into their multimedia curricula, from elementary science lessons featuring animated molecular structures to university-level medical training using 3D anatomical animations. The Khan Academy demonstrates this principle effectively, using simple animated explanations to make complex mathematical and scientific concepts accessible to millions of learners worldwide.
Employee Training
Corporate training programs have embraced animation as a cost-effective solution for employee development and onboarding. Animated training modules can simulate real-world scenarios without the risks and expenses associated with practical training environments.
Animation in training multimedia projects offers several advantages: consistent message delivery, scalable content distribution, and the ability to visualise dangerous or expensive procedures safely. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and aviation rely heavily on animated training content to ensure safety compliance and skill development.
Interactive animated simulations allow employees to practice procedures repeatedly, building confidence and competency before applying skills in real-world situations. This approach reduces training costs while improving learning outcomes and retention rates.
User Engagement
Animation dramatically increases user engagement across digital platforms. Websites incorporating animated elements experience 27% higher click-through rates and 33% longer average session durations compared to static alternatives. These statistics highlight animation’s effectiveness in capturing and maintaining user attention.
Micro-animations, such as loading indicators, button hover effects, and transition animations, improve user experience by providing visual feedback and creating more intuitive interfaces. These subtle animated elements guide users through digital experiences while adding personality and polish to multimedia projects.
Social media platforms prioritise animated content in their algorithms, recognising its superior engagement potential. Videos with animated graphics receive 48% more views and 33% more shares than static posts, making animation essential for social media marketing strategies.
Multimedia Portfolio
For creative professionals, animation capabilities significantly enhance portfolio value and client appeal. Multimedia portfolios showcasing animation skills demonstrate technical proficiency and creative versatility that static work cannot match.
Animation allows portfolio creators to present their work dynamically, showing process development, before-and-after transformations, and creative problem-solving approaches. This dynamic presentation format helps creative professionals stand out in competitive markets and command higher project fees.
Portfolio websites integrating animation receive 45% more client inquiries and demonstrate 60% higher perceived professionalism compared to static alternatives. These metrics underscore animation’s importance for career advancement in creative industries.
Types of Animation
Understanding different animation types helps multimedia creators choose appropriate techniques for specific project goals and audience preferences.
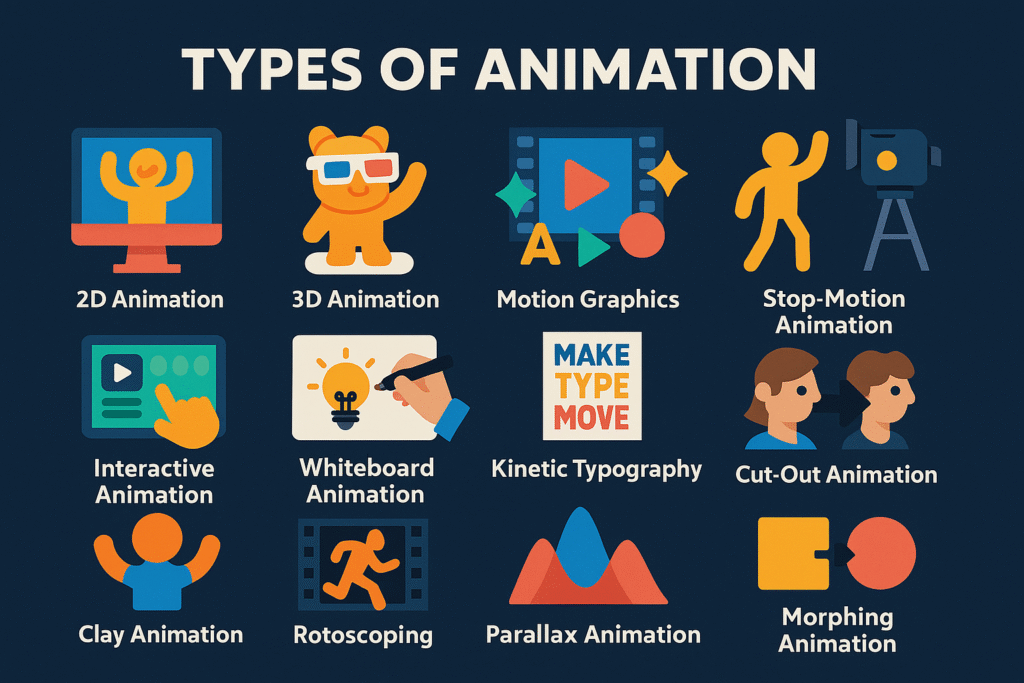
2D Animation remains popular for its accessibility and cost-effectiveness. From simple motion graphics to complex character animations, 2D techniques work well for educational content, marketing videos, and explainer multimedia projects. Tools like After Effects and Animate CC make 2D animation accessible to creators with varying skill levels.
3D Animation provides realistic visualisations ideal for product demonstrations, architectural presentations, and scientific explanations. While more resource-intensive than 2D alternatives, 3D animation creates immersive experiences that enhance audience understanding and engagement.
Motion Graphics combine typography, shapes, and visual elements to create compelling animated designs. This technique excels in multimedia projects requiring clear information delivery, such as data visualisations, corporate presentations, and social media content.
Stop-Motion Animation offers unique aesthetic appeal through its handcrafted appearance. While time-intensive, stop-motion creates memorable visual experiences that stand out in crowded digital environments.
Interactive Animation responds to user input, creating engaging experiences in web design, mobile applications, and educational multimedia. This type enables personalised user journeys and enhanced engagement through participation rather than passive consumption.
Whiteboard Animation simulates the process of drawing on a whiteboard, making it perfect for educational content and explainer videos. This style creates a sense of real-time learning and keeps viewers engaged as they watch concepts develop step by step.
Kinetic Typography brings text to life through movement, timing, and visual effects. This animation type works exceptionally well for quote animations, lyric videos, and content where the message is primarily text-based but needs visual impact.
Cut-Out Animation uses flat characters and backgrounds that move like paper dolls, creating a distinctive layered look. Popular in shows like South Park, this technique offers cost-effective character animation for multimedia projects with limited budgets.
Clay Animation (Claymation) uses malleable clay figures that are photographed frame by frame. This tactile animation style creates warm, organic-feeling content that works well for children’s content and artistic projects.
Rotoscoping involves tracing over live-action footage to create realistic animated movement. This technique bridges the gap between live-action and animation, creating fluid, lifelike motion that’s perfect for complex human movements.
Parallax Animation creates depth by moving background and foreground elements at different speeds. Common in web design and scrolling websites, this technique adds visual interest without requiring complex character animation.
Morphing Animation transforms one shape or object into another through smooth transitions. This technique works well for logo animations, product transformations, and abstract concept explanations in multimedia presentations.
Benefits of Using Animation in Multimedia Projects
The integration of animation into multimedia projects delivers measurable benefits that directly impact how audiences interact with and remember your content.
Attracts Attention Instantly is animation’s most immediate benefit. Moving elements naturally draw the human eye, with animated content receiving 94% more views than static images. The brain’s motion detection system automatically focuses on animated elements, making them powerful attention-grabbers in crowded digital spaces. This biological response means animated multimedia projects consistently outperform static alternatives in capturing initial user interest.
Increases User Engagement Significantly through interactive and visually appealing content. Websites with animated elements see 27% higher click-through rates and users spend 33% more time on pages containing animation. The dynamic nature of animation encourages users to interact, scroll, and explore content more thoroughly. Social media posts with animated graphics generate 48% more engagement than static posts, demonstrating animation’s power to create meaningful user interactions.
Improves Memory Retention Dramatically by activating multiple cognitive pathways simultaneously. The human brain processes visual information 60,000 times faster than text, and animated content creates stronger memory associations through the dual coding theory. Viewers retain 95% of information from animated content compared to only 10% from text alone. This occurs because animation engages both visual and auditory processing centers, creating multiple memory triggers that improve long-term recall.
Enhances Learning and Comprehension by making complex concepts more accessible. Educational content with animation increases understanding by up to 400% compared to traditional text-based materials. Animation breaks down abstract ideas into visual sequences that learners can process step-by-step. This visual scaffolding helps audiences build mental models of complex processes, leading to deeper understanding and better knowledge transfer.
Builds Emotional Connections through storytelling and character development. Animated elements trigger emotional responses that create lasting impressions and brand loyalty. The mirror neuron system in our brains responds to animated characters and movements as if they were real, generating empathy and emotional engagement. This psychological response makes animated multimedia projects more memorable and persuasive than purely informational content.
Maintains User Interest Longer by providing continuous visual stimulation. The average human attention span online is 8 seconds, but animated content can extend viewing time by 200-300%. Animation prevents visual fatigue by introducing movement and change, keeping users engaged throughout longer content pieces. This extended engagement time allows for more complete message delivery and better conversion rates.
Simplifies Complex Information by breaking down complicated processes into digestible visual chunks. Animation can demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships, show temporal sequences, and illustrate spatial relationships that text cannot convey effectively. This visual simplification reduces cognitive load, making information more accessible to diverse audiences with varying educational backgrounds and learning preferences.
The Motion Graphics Collective regularly showcases how professional animation enhances multimedia project effectiveness across industries, providing inspiration and technical insights for creators seeking to improve their animated content quality..
Conclusion
Animation has become an important part of modern multimedia projects, helping creators communicate more effectively with their audiences. Throughout this guide, we’ve seen how animation in multimedia serves different purposes – from making complex topics easier to understand to keeping viewers engaged longer.
The applications we’ve covered show that animation works well across many industries and project types. Whether you’re building educational content, training materials, or marketing campaigns, adding animated elements can make your message clearer and more memorable.
Different animation techniques offer various benefits depending on your needs and budget. Simple motion graphics might work perfectly for one project, while 3D animation could be the right choice for another. The key is matching the technique to your goals and audience.
What makes animation particularly valuable is its ability to improve user experience while supporting business objectives. Better engagement, clearer communication, and stronger brand recognition are practical benefits that many multimedia projects can achieve through thoughtful animation use.
As more content competes for attention online, animation provides a way to stand out while delivering real value to your audience. The tools and techniques are more accessible now than ever before, making it easier for creators to experiment and find what works best for their projects.
If you’re considering adding animation to your multimedia work, start small. Test simple animated elements and see how your audience responds. You might find that even basic animations can make a meaningful difference in how people connect with your content.
FAQs
What is the difference between animation and multimedia?
Animation refers specifically to the technique of creating moving images through sequential frames or digital manipulation. Multimedia is a broader concept encompassing the integration of various media types including text, audio, video, images, and animation. Animation becomes one component within multimedia projects, working alongside other elements to create comprehensive digital experiences.
How does animation improve learning in educational multimedia?
Animation improves educational outcomes by appealing to visual and kinesthetic learning styles, increasing information retention by up to 65%, and making abstract concepts concrete through visual representation. Animated educational content activates multiple cognitive pathways simultaneously, creating stronger memory associations and deeper understanding compared to static materials.
What types of animation work best for business multimedia projects?
Business multimedia projects typically benefit from motion graphics for data visualisation, 2D animation for explainer videos, 3D animation for product demonstrations, and micro-animations for website user experience. The choice depends on project goals, target audience, budget constraints, and brand positioning requirements.
Is animation expensive to include in multimedia projects?
Animation costs vary significantly based on complexity, duration, and production method. Simple motion graphics and micro-animations can be cost-effective, while complex 3D animations require larger investments. However, animated assets can be repurposed across multiple platforms and updated easily, often providing better long-term value than live-action alternatives.
How can I measure the effectiveness of animation in my multimedia projects?
Key metrics for measuring animation effectiveness include engagement rates (time spent viewing content), interaction rates (clicks, shares, comments), retention rates (completion percentages), conversion rates (desired actions taken), and user feedback scores. Analytics tools can track these metrics across different platforms to assess animation’s impact on project success.
What software is recommended for creating animations for multimedia projects?
Popular animation software options include Adobe After Effects for motion graphics, Adobe Animate for 2D animation, Blender for 3D animation (free), Cinema 4D for professional 3D work, and Lottie for web-optimised animations. The choice depends on project requirements, skill level, budget, and integration needs with other multimedia elements.
Can animation improve SEO for multimedia content?
Yes, animation can improve SEO through increased user engagement metrics such as longer session durations, lower bounce rates, higher click-through rates, and more social shares. Search engines interpret these positive user behaviour signals as quality indicators, potentially improving content rankings and visibility in search results.
How long should animations be in multimedia projects?
The ideal animation length depends on context and purpose. For web micro-animations, 200-500 milliseconds works best to provide feedback without slowing user experience. Social media animations perform well at 6-15 seconds, matching platform algorithms and attention spans. Educational animations can be longer (30 seconds to 2 minutes) as they serve instructional purposes. Loading animations should complete within 2-3 seconds to avoid user frustration. The key is matching duration to user expectations and content goals while maintaining engagement throughout the entire sequence.